Toolkit: Complex Systems Toolkit.
Toolkit: Complex Systems Toolkit.
Author: Professor Nici Zimmermann (University College London).
Topic: Illuminating complex interactions in a system through participatory modelling methods.
Title: Using a participatory modelling approach to urban regeneration.
Resource type: Teaching activity.
Relevant disciplines: Any; civil engineering.
Keywords: Available soon.
Licensing: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Related INCOSE Competencies: Toolkit resources are designed to be applicable to any engineering discipline, but educators might find it useful to understand their alignment to competencies outlined by the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE). The INCOSE Competency Framework provides a set of 37 competencies for Systems Engineering within a tailorable framework that provides guidance for practitioners and stakeholders to identify knowledge, skills, abilities and behaviours crucial to Systems Engineering effectiveness. A free spreadsheet version of the framework can be downloaded.
This resource relates to the Systems Thinking, Systems Modelling and Analysis and Critical Thinking INCOSE competencies.
AHEP mapping: This resource addresses several of the themes from the UK’s Accreditation of Higher Education Programmes fourth edition (AHEP4): Analytical Tools and Techniques (critical to the ability to model and solve problems), and Integrated / Systems Approach (essential to the solution of broadly-defined problems). In addition, this resource addresses the AHEP themes of Design and Practical and workshop skills.
Educational level: Intermediate or advanced.
Learning and teaching notes:
This activity is suitable for those having acquired some familiarity with complex systems and related concepts – especially causal loop diagrams, stock and flow diagrams, cognitive maps or participatory maps – who are looking for additional ideas for activities or who have a specific interest in participatory modelling. The activity is also useful at the point when students learn about interaction between different elements of a complex system or when they learn about the importance of human factors.
Learners have the opportunity to:
- Deepen their understanding of systems thinking.
- Engage with participatory modelling.
- Enjoy a fun group activity.
Teachers have the opportunity to:
- Introduce students to participatory modelling (i.e. more specifically to participatory system dynamics / group model-building).
- Develop students’ understanding of stock-and-flow modelling in the tradition of system dynamics.
- Support students’ understanding of complex interactions around urban dynamics, and if adapted also around other contexts.
Downloads:
- A PDF of this resource will be available soon.
Learning and teaching resources:
- Pre-reading: One or several of the following resources on developing causal loop diagrams and stock and flow models:
-
- To bring students up to speed with causal loop diagrams and stock and flow diagrams:
-
-
- Deaton & MacDonald, 2025: System Dynamics Learning Guide, chapters 1–2.
-
-
- Resources on group model-building:
-
-
- Andersen & Richardson, 1997: Scripts for group model building.
-
- Additional reading:
-
- On causal loop diagrams and stock and flow diagrams:
-
-
- Meadows, 2008: Thinking in Systems: A Primer.
-
-
-
- Sterman, 2000: Business Dynamics, chapters 1–6.
-
-
- On group model-building:
-
-
- Richardson & Andersen, 1995: Teamwork in group model building.
-
-
-
- Vennix, 1996: Group Model Building.
-
-
-
- Hovmand, 2014: Community based system dynamics.
-
-
-
- Antunes et al., 2015: Using participatory system dynamics in environmental and sustainability dialogues
-
-
- On the London Docklands:
-
-
- Church, 1987: Urban regeneration in London Docklands: a five-year policy review.
-
-
- Teaching practice paper that this activity is based on:
Overview:
This activity introduces students to a participatory systems thinking – or more specifically – participatory modelling exercise. This is an approach used in group settings to explore complex issues and represent them via models. In this activity, students assume the roles of stakeholders involved in an urban regeneration project and take part in a group model-building workshop.
It teaches students core principles of a participatory modelling method called group model-building or participatory system dynamics, but it can also be used to teach the underlying system structure of a specific phenomenon. This makes it well-suited for modules that contain elements of systems thinking and system dynamics (including causal loop diagramming and simulation modelling) or modules that contain an element on group facilitation and participatory methods.
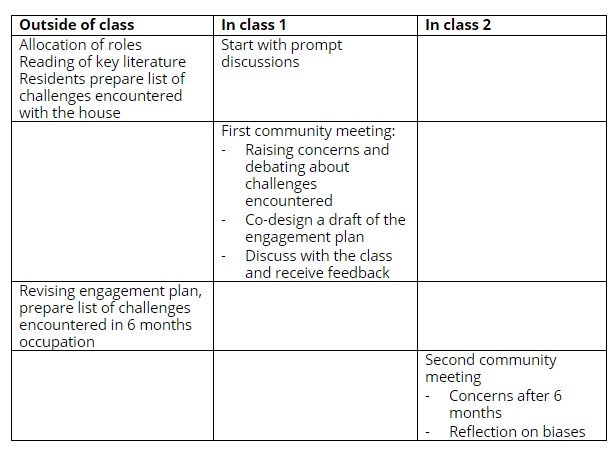
The activity is designed to run over 1.5 to 2.5 hours and is adaptable. While the current example focuses on the phenomenon of urban dynamics around the population development in a city, the activity can be reframed using a case and model from a project management, water management, energy or other sustainability-related context.
The activity is directly aligned with systems thinking by immersing students in a participatory modelling process. It develops students’ awareness of system content and its interactions by teaching them qualitative modelling skills. It develops their skills in managing complexity and representing system elements with visual models consisting of items and their relationships depicted in causal loop diagrams and/or stock and flow diagrams. This serves to build students’ analysis skills and ability to apply systems approaches to problems. It also develops their practitioner, practical and workshop skills of collaborating with stakeholders. It does so by advancing their facilitation skills essential for collaborative systems work. This includes rules of conduct and techniques for managing a group discussion and group dynamics, making a broad range of ideas heard, prioritising them and mapping them visually.
Materials or software required:
- Resources on population trajectories:
- If using a blackboard/whiteboard:
For in-person sessions, the following materials are recommended:
- If projecting a screen using software or for online or hybrid formats (for teachers familiar with mapping or modelling software):
-
- System dynamics software, such as:
-
-
- Vensim PLE (free for academic use)
-
-
-
- Stella (commercial, with educational licenses available)
-
-
-
- Kumu (offers a free version for basic mapping)
-
-
- Collaborative mapping tools, such as:
-
-
- Miro (free version available with up to three active boards)
-
-
-
- MURAL or similar platforms (depending on institutional access)
-
If software or an online tool are used, these are used to collate concepts (variables suggested by students) and to build a diagram of their interactions. This will be projected to the in-person and/or online participants, replicating the participatory nature of in-person workshops.
Detailed explanation of the activity:
This activity introduces students to participatory modelling, an approach used in group settings to explore and understand complex issues and represent them via models. In this case, participatory modelling is introduced through a structured group model-building workshop, using a simplified version (Alfeld & Graham, 1976; Richardson, 2014) of Jay Forrester’s (1969) famous Urban Dynamics model, which sparked quite some debate because of its counter-intuitive insights. The session begins with a brief historical overview of urban growth and decline in major cities up to the 1980s (e.g. New York, Boston, London; see files under ‘Downloads’, above), before focusing on the London Docklands in London in 1981, as an example of an opportunity for urban redevelopment to counter the trend of population decline. Student groups are assigned stakeholder roles from that time, including the founder of the London Docklands Development Corporation (1–2 students), the Surrey Quays Housing Action Group (2–6 students), the London Chamber of Commerce (2–6 students) and the Greater London Council (2–6 students). Each student group receives a role sheet outlining their perspective and a small set of key variables relevant to their stakeholder position (see linked files). These variables are intentionally curated to align with the Urban Dynamics model and to ensure that collaboration is necessary to draw the interlinkages between the variables, i.e. the relevant system structure.
A list of variables provided to the student groups via the role sheets is included below. Note that not all variables that are necessary to draw the model are included; students need to infer a few variables to train their thinking.
- London Docklands Development Corporation
-
- Population (This is the total number of people living in the city. As the variable represents the sum of all people, it is an integral. Specific pictogram language can highlight this. In the tradition of system dynamics modelling, one would therefore put a rectangle around it, which the teacher can do after the variable has been placed on the board.)
- Surrey Quays Housing Action Group
-
- Housing Structures (Indicates the number of dwellings. Housing is important for urban development. As the variable represents the sum of all dwellings, it is also an integral, which would be depicted by a rectangle.)
-
- Ratio of households to housing (This variable is an indicator of crowding. Ideally, there is one household per housing structure. A number above one means that some people need to live in shared places. A number below one means that there is vacant housing.)
- London Chamber of Commerce
-
- Business structures (Indicates the number of business units. Businesses are important to urban development. As the variable represents the sum of all business units, it is also an integral, which would be depicted by a rectangle.)
-
- Jobs (Total number of jobs available in the city (whether filled or unfilled).
- Greater London Council
-
- Population (Repeated variable to be able to compare between groups.)
-
- Net migration (Change in population. The simple model excludes population changes by births and deaths because of the relative larger changes by national and international migration.)
-
- Jobs (Repeated variable to be able to compare between groups.)
Before the workshop begins, students are introduced to core concepts of participatory modelling (see linked slides), including facilitator roles (based on Richardson & Andersen, 1995) and common workshop scripts (e.g. hopes and fears, variable elicitation, voting, model building, policy option elicitation and system storytelling, as described in Scriptapedia and Andersen & Richardson, 1997).
The workshop proceeds in three main phases:
1. Variable elicitation: After a short introduction by the student playing the founder of the London Docklands Development Corporation into the setting and by the facilitator/teacher into the process, each group sketches behaviour-over-time graphs of their assigned variables (10 minutes). These are presented using a round-robin or nominal group technique, meaning one variable per group at a time only, and placed on a whiteboard/blackboard or digital canvas. The round-robin collection is a technique useful to foster inclusivity and avoid talking heads. Behaviour-over-time graphs rather than just variable names are useful because the final model is believed to explain a behavioural trend over time, linking model structure and dynamics. However, it is also possible to simplify by letting students just write the variable names on sheets of paper.
2. Voting and prioritisation: To decide on a starting point for modelling, each student votes on which variables they consider to be the most important to include in the model, e.g. giving the students as many votes as there are variables on the board and freedom of how to distribute their votes. While all variables will be included in the model, the voting activity provides a basis for reflection on different priorities and students’ personal vs. their group’s perspective, after the modelling activity.
3. Model building: The class collaboratively constructs a stock and flow diagram (see Figure 1). Stocks such as Housing Structures, Business Structures, and Population are identified, and their net rates of change are discussed. To connect the variables, some more variables need to be added such as the ratio of population to jobs, total land available, and land occupied. To help students identify these variables, the teacher can ask questions: “Population and housing are linked by a ratio. What concepts and respective variables could link the other stocks?”. Students are encouraged to identify feedback loops and classify them as reinforcing or balancing.
It is useful to pay attention to uncovering less obvious relationships, such as the spatial competition between housing and business infrastructure. Once the diagram is complete, the facilitator reviews the model with the class, highlighting key feedback structures.
After the modelling activity, students can be shown images of the Docklands after the redevelopment as well as urban population trends of London and other major cities until today, prompting discussion on the long-term impacts of different types of development and prioritisation of a business vs. housing focus. The session can conclude with a reflection on the participatory process and its relevance to real-world decision-making and the value of participatory modelling in complex policy environments.
A more comprehensive version of this activity – including a more introductory group model-building exercise that teaches basic causal loop diagramming concepts and an alternative context using project management as an example – is available: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10160261/
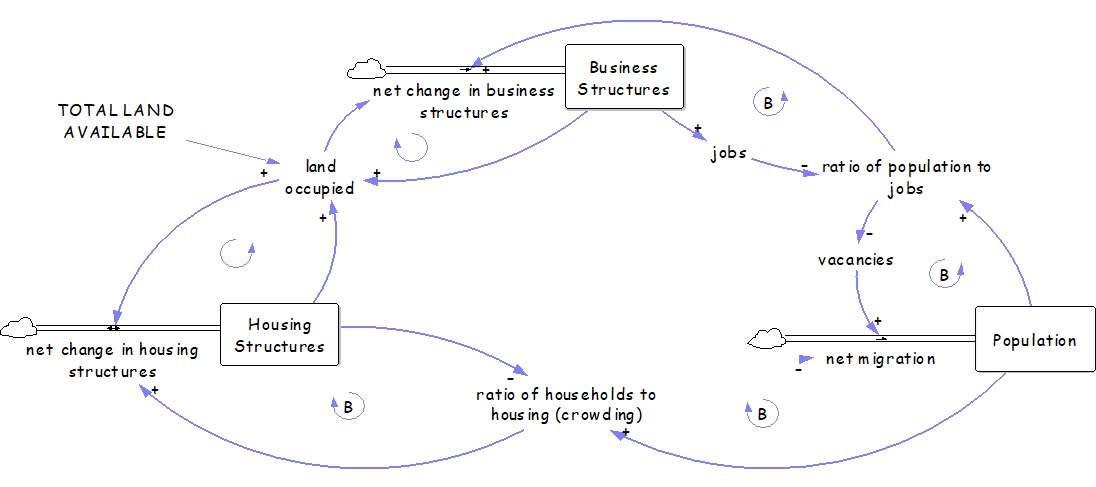

Figure 1: Stock and flow diagram of urban dynamics (produced with Vensim software). This figure is intended for educators and serves an illustrative purpose. It provides educators with a reference for how the model built during the activity is expected to look.
Note: The author was originally inspired to focus on this case by the historical accounts found on the London Docklands Development Corporation (LDDC) History Pages (http://www.lddc-history.org.uk/index.html, now inactive).
References:
- Alfeld LE, & Graham AK. 1976. Introduction to Urban Dynamics. Cambridge, MA: Productivity Press.
- Andersen DF, & Richardson GP. 1997. Scripts for group model building. System Dynamics Review 13(2): 107–129.
- Antunes P, Stave K, Videira N, & Santos R. 2015. Using participatory system dynamics in environmental and sustainability dialogues. In M. Ruth (Ed.), Handbook of Research methods and Applications in Environmental Studies. Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK: 346–374.
- Deaton M, & MacDonald R. 2025. System Dynamics Learning Guide. Harrisonburg, VA: James Madison University Libraries.
- Forrester JW. 1969. Urban Dynamics. Cambridge, MA: M.I.T. Press.
- Hovmand PS. 2014. Community based system dynamics: Springer.
- Meadows D. 2008. Thinking in Systems–A Primer. White River Junction, VT: Chelsea Green Publishing.
- Richardson GP. 2014. “Model” teaching II: Examples for the early stages. System Dynamics Review 30(4): 283–290.
- Richardson GP, & Andersen DF. 1995. Teamwork in group model building. System Dynamics Review 11(2): 113–137.
- Sterman JD. 2000. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. Boston, MA: Irwin/McGraw-Hill.
- Vennix JAM. 1996. Group Model Building: Facilitating Team Learning Using System Dynamics. Chichester, NY: Wiley.
- Zimmermann, N. 2026 (forthcoming). Weaving participatory modelling into teaching: Purposes and practices from system dynamics education. Systems Dynamics Review.
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.