Theme: Graduate employability and recruitment, Collaborating with industry for teaching and learning, Knowledge exchange
Theme: Graduate employability and recruitment, Collaborating with industry for teaching and learning, Knowledge exchange
Authors: Dr Corrina Cory (University of Exeter), Nick Russill (University of Exeter and Managing Director TerraDat UK Ltd.) and Prof Steve Senior (University of Exeter and Business Development Director at Signbox Ltd.)
Keywords: Gold Standard Project Based Learning, EntreComp, 21st Century Skills, Entrepreneur in Residence, Collaboration
Abstract: We have recently updated our engineering programmes at the University of Exeter (E21 – Engineering the Future) with a USP of Entrepreneurship at the core of the first two years to prepare students for research led learning and the future of jobs. We have worked closely with our Royal Society Entrepreneurs in Residence (EiR) to ensure authenticity in our ‘real-world’ Gold Standard Project Based Learning (GSPBL) activities. We would like to share this great collaboration experience with our EPC colleagues.
Introduction
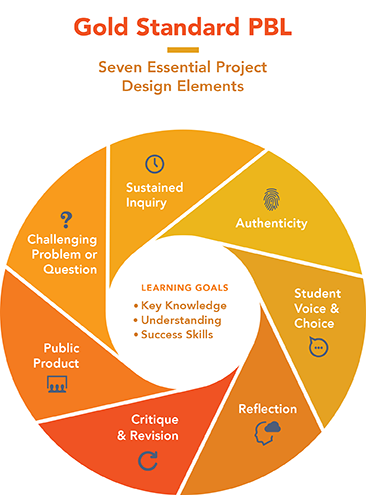
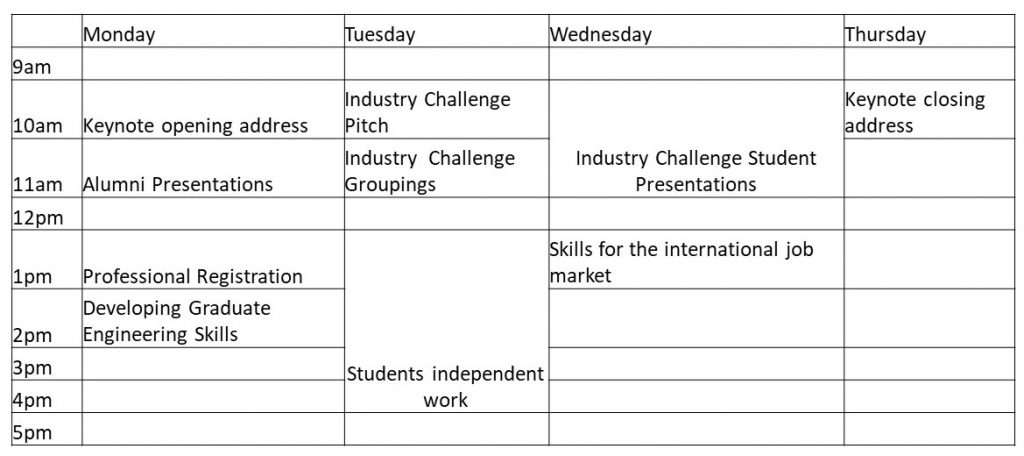
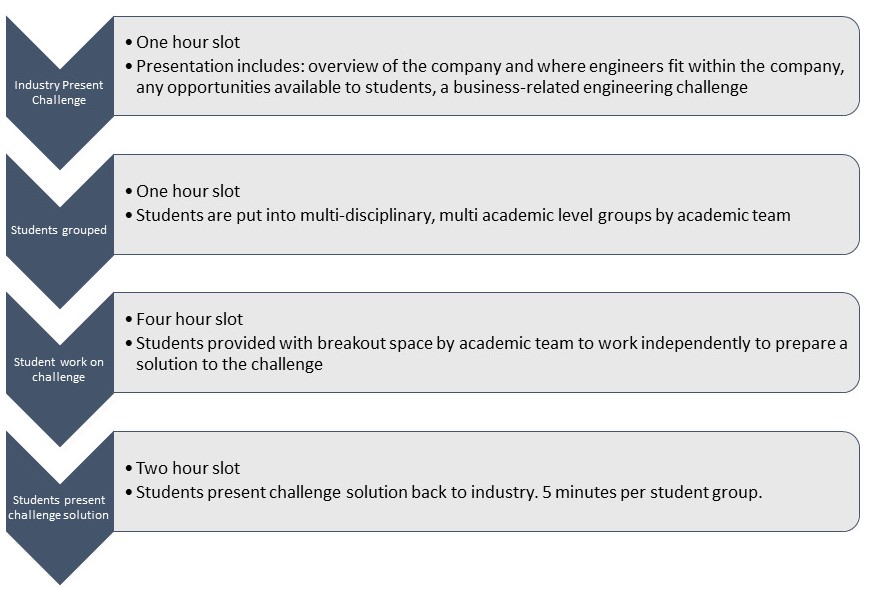
We have recently updated our engineering programmes at The University of Exeter (E21 – Engineering the Future). The Unique Selling Point (USP) of Entrepreneurship is embedded through Stage 1 and 2 using a new methodology combining Gold Standard Project Based Learning (GSPBL)[1] [image: Picture_1.jpg]) and EntreComp[2] ([image: Picture_2.png], the European Entrepreneurship Competence Framework).[3-5]
Gold Standard PBL – Seven Essential Project Design Elements [4]. Creative Commons License. Reference [1] – pblworks.org (2019). Gold Standard PBL: Essential Project Design Elements. [online] Available at: www.pblworks.org/what-is-pbl/gold-standard-project-design (Accessed 16 February 2022).
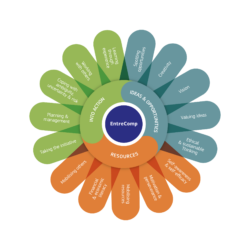

The EntreComp wheel: 3 competence areas and 15 competences [5]. Creative Commons License. Reference [2] – McCallum, E., Weicht, R., McMullan, L., Price, A. (2018). EntreComp into Action: get inspired, make it happen, M. Bacigalupo & W. O’Keeffe Eds., EUR 29105 EN, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, pg.13, pg. 15 & pg. 20.
The 21st Century Skills developed in the early stages of the programmes prepare students for research-led learning in later stages and future graduate employment.
The Royal Society Entrepreneur in Residence (EiR) scheme, aims to increase the knowledge and awareness of cutting-edge industrial science, research and innovation in UK universities. The scheme enables highly experienced industrial scientists and entrepreneurs to spend one day a week at a university developing a bespoke project.
In this context, the EiR scheme has grown ‘confidence in, and understanding of business and entrepreneurship among staff and students’ and we have collaborated with our EiRs to ensure authenticity in our ‘real-world’ project-based learning activities.[6] They have inspired students to pursue their own ideas and bring them to reality in ways that bring sustained regional and global benefit.
Aims
- Develop collaborative relationships with EiRs.
- Implement our newly developed methodology combining GSBPL and EntreComp to thread a USP of Entrepreneurship throughout our updated engineering programmes.
- Integrate the experience of our EiRs via Entrepreneurship modules in experiential project launches, interactive workshops and attendance at pitch presentations.
- Update assessments to include multi-media, entrepreneurial submissions including storyboards, video pitches, wireframes and websites to assess digital competency, creativity, business, collaboration and inclusivity for successful future graduate employment.
Plan
The Engineering Department worked with venture capitalist Alumni, Adam Boyden to create a MEng in Engineering & Entrepreneurship. The education team seized the opportunity during curriculum development to make the Stage 1 and 2 Entrepreneurship modules common to all engineering programmes to embed a USP of Entrepreneurship in E21.
Both our EiRs are natural educators and thrive on sharing their rich experiences and stories to mentor others through their entrepreneurship journeys.
They provide on-site technology demonstrations, prizes for 21st Century Skills and interactive workshops on entrepreneurship. This integration of EiRs into teaching and learning adds variety, and through the power of story, the students engage to a high level. Furthermore, their curiosity prompts them to construct and ask challenging questions.
The open-ended GSPBL driving questions allow groups to develop unique ideas. Most of the projects yielded excellent and highly original themes, some of which could have real value in the future should they be further developed.
We have observed learning opportunities for inclusivity, listening, improvements in self-confidence and more free-thinking and ideation as a direct result of our methodology combining GSPBL and EntreComp.
Using this method and mapping competences using EntreComp should improve outcomes for graduates who gain the top employability skills required by 2025 e.g., critical thinking and analysis, problem-solving, self-management, active learning, resilience, stress tolerance and flexibility.[7] Students develop an appreciation and understanding of business start-ups, ideation and successful implementation of innovative research and development through their experiential learning.
Outcomes
Our EiRs have provided insights into what it takes to be an entrepreneur and have introduced energy, enthusiasm, creativity and innovative thought processes throughout both Entrepreneurship modules.
Nick Russill’s specific contributions include team building, planning, branding, entrepreneurial skills, innovation, business development, co-hosting project launch seminars, innovation workshops, project-based learning support sessions and mock investment pitch panels.
Steve Senior’s lectures Q&As and workshops include the beauty of failure, advanced Computer Aided Design (CAD)/Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM), marketing and e-commerce. He mentors student teams on how to capitalise on limited resources during growth and explains risk analysis with case studies from his own companies.
The digital materials created for our blended updated programmes will remain a longer-term legacy of their involvement and provide resources available to be called on in future to sustain the impact of EiRs at Exeter.
Nick has commented that ‘my time as EiR with the Exeter engineering students has convinced me that GSPBL takes education to another level, and I wish it were more widespread in education curricula … The close association of learning with real-life applications and case studies has proved that students retain far more technical and theoretical information than they may do from more traditional methods’.
Students are surveyed at the start of Entrepreneurship 1 and the end of Entrepreneurship 2 in terms of their self-assessed ability to evidence aspects of EntreComp on their CV. Previous publications have illustrated an increase in competence over the 2 years of Entrepreneurship and we will continue to collect this data to evidence outcomes.[5]
Entrepreneurs in residence share their real-world experience and then stick around to build relationships with the staff, researchers and students. They become an integral part of the team. Student Feedback definitely proves that we’re helping to ignite sparks for a new generation of entrepreneurs. Student feedback includes:
‘Gain skills in areas concerning self-motivation and creativity’… ‘become comfortable with risk and uncertainty … a really good learning experience’ …’developing confidence and being able to trust yourself and take the initiative’… ‘good innovation and technical skills’ … ‘learning by doing is the only way for entrepreneurship and this course has given us a great environment and support to learn, fail, pivot and learn again’.
Staff and students have commented on the value of injecting ad hoc real-life anecdotes of problem-solving stories and learnings from experienced entrepreneurs which is unique, valuable and significantly enriches learning experiences.
Lessons and Future Work
An individual reflective work package report is submitted by all students at the completion of two years of entrepreneurship modules. This provides a period of reflection for students and a chance to showcase their journey including valuable learning through failure, personal contributions to the group’s success and professional development in terms of 21st Century Skills as defined by EnreComp.
Following panel Q&A at the EPC Crucible Project, future refinement includes reviewing possible additions to the reflective report and illustrating links between engineering competence and EntreComp to clearly signpost students to the relevance of Entrepreneurial 21st Century Skills for graduate employment, chartership and intrapreneurship.
References
- pblworks.org, 2019. Gold Standard PBL: Essential Project Design Elements. [online] PBLWorks. Available at: https://www.pblworks.org/blog/gold-standard-pbl-essential-project-design-elements (Accessed 18 February 2022).
- European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Price, A., McCallum, E., McMullan, L., et al. (2018) EntreComp into action : get inspired, make it happen. Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/574864, pp.13, 15 & 20.
- Cory, C., Carroll, S. and Sucala, V., 2019. Embedding project-based learning and entrepreneurship in engineering education. In: New Approaches to Engineering Higher Education in Practice. Engineering Professors’ Council (EPC) and Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) joint conference.
- Cory, C., Sucala, V. and Carroll, S., 2019. The development of a Gold Standard Project Based Learning (GSPBL) engineering curriculum to improve Entrepreneurial Competence for success in the 4th industrial revolution. In: Complexity is the new Normality.. Proceedings of the 47th SEFI Annual Conference, pp.280-291.
- Cory, C. and Cory, A., 2021. Blended Gold Standard Project Based Learning (GSPBL) and the development of 21st Century Skills – an agile teaching style for future online delivery. In: Teaching in a Time of Change. AMPS Proceedings Series 23.1., pp.207-217.
- Royalsociety.org, 2022. Entrepreneur in Residence | Royal Society. (online) Royalsociety.org. Available at: https://royalsociety.org/grants-schemes-awards/grants/entrepreneur-in-residence/ (Accessed 18 February 2022).
- World Economic Forum. 2020. The Future of Jobs Report 2020. [online] Available at: https://www.weforum.org/reports/the-future-of-jobs-report-2020 (Accessed 18 February 2022).
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.