 Theme: Collaborating with industry for teaching and learning, Graduate employability and recruitment
Theme: Collaborating with industry for teaching and learning, Graduate employability and recruitment
Author: James Ford (University College London)
Keywords: Civil Engineering Design, Timber Design, Industry, Collaboration
Abstract: A project, developed jointly by UCL and engineers from ARUP, allowed students to work on redesigning the fire damaged roof of the Notre Dame Cathedral. Industry expertise complemented academic experience in civil engineering design to create a topical, relevant and creative project for students. The project combined technical learning in timber design with broader considerations such as costs, health and safety, buildability and environmental impacts. Final presentations being made to engineering teams at ARUP offices also developed wider professional skills.
Background
Following the 2019 fire in the Notre Dame Cathedral, Civil Engineering Students at University College London (UCL) were tasked with designing a replacement. The project was delivered, in collaboration with engineers from ARUP, within a Design module in Year 2 of the programme. The project was run as a design competition with teams competing against one another. The project built on learning and design project experience built up during years 1 and 2 of the course.
The collaboration with ARUP is a long-standing partnership. UCL academics and ARUP engineers have worked on several design projects for students across all years of the Civil Engineering Programme.
The Brief
Instead of designing a direct replacement for the roof the client wanted to create a modern, eye-catching roof extension which houses a tourist space that overlooks the city. The roof had to be constructed on the existing piers so loading limits were provided. The brief recognised the climate emergency and a key criterion for evaluation was the sustainability aspects of the overall scheme. For this reason, it also stipulated that the primary roof and extension structure be, as far as practicable, made of engineered timber.
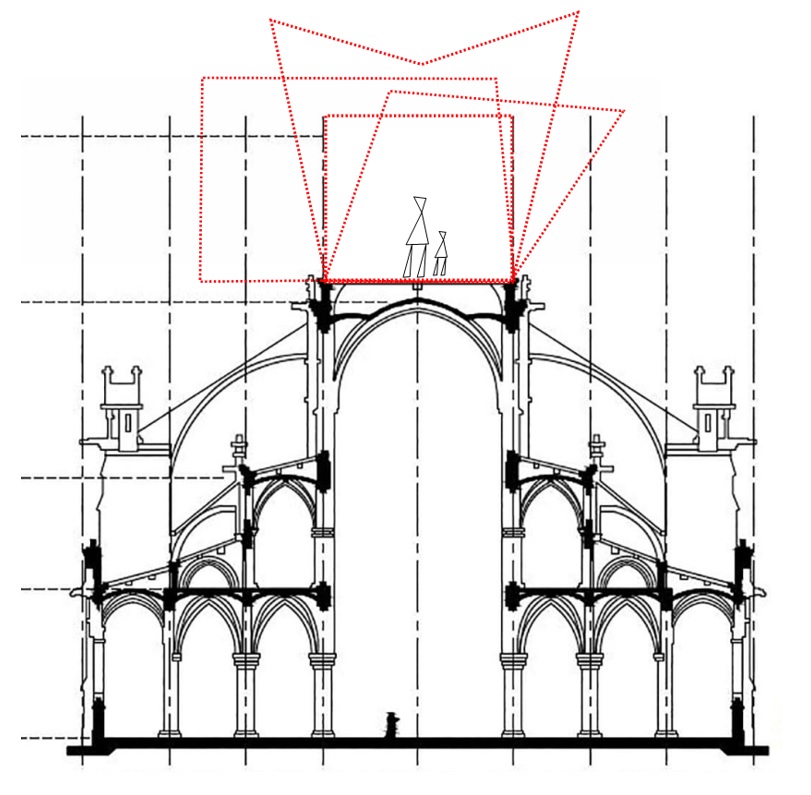
Figure 1. Image from the project brief indicating the potential building envelopes for the roof design
Given the location all entries had to produce schemes that were quick to build, cause minimal disruption to the local population, not negatively impact on tourism and, most importantly, be safe to construct.
Requirements
Teams (of 6) were required to propose a minimum of 2 initial concept designs with an appraisal of each and recommendation for 1 design to be taken forward.
The chosen design was developed to include:
- Full structural design; Calculations to Eurocodes, load path diagrams, member sizing, connection design, explanation of structural choices.
- Buildability (cost breakdown, site logistics, consideration of context)
- Health and Safety risks, impacts on design and control measures
- Construction sequence
- Sustainability summary inc. embodied carbon calculations
Teams had to provide a 10xA3 page report, a set of structural calculations, 2xA3 drawings and a 10-minute presentation.
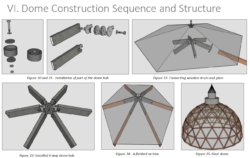

Figure 2. Connection detail drawing by group 9
Delivery
Course material was delivered over 4 sessions with a final session for presentations:
Session 1: Project introduction and scheme designing
Session 2: Timber design
Session 3: Construction and constructability
Session 4: Fire Engineering and sustainability
Session 5: Student Presentations
Sessions were co-designed and delivered by a UCL academic and engineers from ARUP. The sessions involved a mixture of elements incl. taught, tutorial and workshop time. ARUP engineers also created an optional evening workshop at their (nearby) office were groups or individuals could meet with a practicing engineer for some advice on their design.
These sessions built on learning from previous modules and projects.
Learning / Skills Development
The project aimed to develop skills and learning in the following areas:
- Technical skills relating to structural design using timber, embodied energy calculations, drawing and H&S risk assessment.
- Design skills relating to consideration of the site, its context and the need, creativity and assessing ideas, consideration and overlapping of numerous disciplines, design iteration and improvement.
- Professional skills in relation to communicating with clients, producing reports to a professional standard, presenting a project, working in teams, organising resources, etc.
Visiting the ARUP office and working with practicing engineers also enhanced student understanding of professional practice and standards.
Benefits of Collaborating
The biggest benefit to the collaboration was the reinforcement of design approaches and principles, already taught by academics, by practicing engineers. This adds further legitimacy to the approaches in the minds of the students and is evidenced through the application of these principles in student outputs.
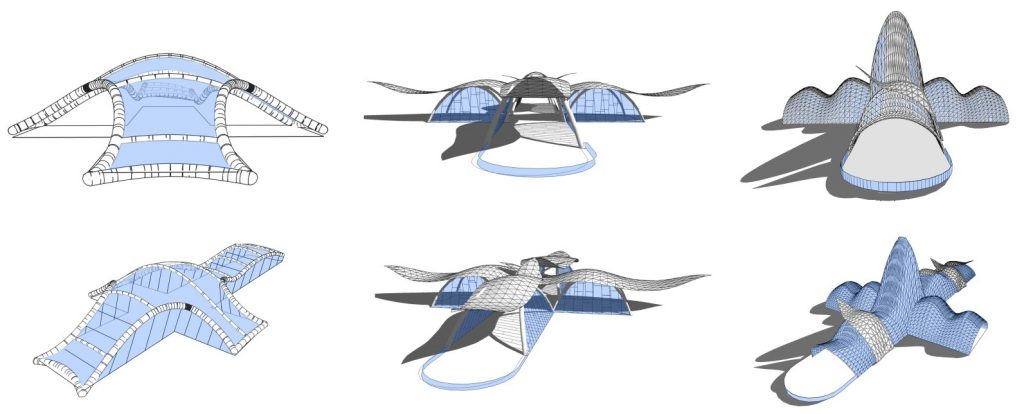
Figure 3. Development of design concepts by group 12
The increased range in technical expertise that such a collaboration brings provides obvious benefit and the increased resource means more staff / student interaction time (there were workshops where it was possible to have one staff member working with every group at the same time).
Working with an aspirational partner (i.e. somewhere the students want to work as graduates) provides extra motivation to improve designs, to communicate them professionally and impress the team. Working and presenting in the offices of ARUP also helped to develop an understanding of professional behaviour.
Reflections and Feedback
Reflections and feedback from all staff involved was that the work produced was of a high quality. It was pleasing to see the level of creativity that the students applied in their designs. Feedback from students gathered through end of module review forms suggested that this was due to the level of support available which allowed them to develop more complex and creative designs fully.
Wider feedback from students in the module review was very positive about the project. They could see that it built on previous experiences from the course and enjoyed that the project was challenging and relevant to the real world. They also valued the experiences of working in a practicing design office and working with practicing engineers from ARUP. Several students posted positively about the project on their LinkedIn profiles, possibly suggesting a link between the project and employability in the minds of the students.

Figure 4. Winning design summary diagram by group 12
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.




