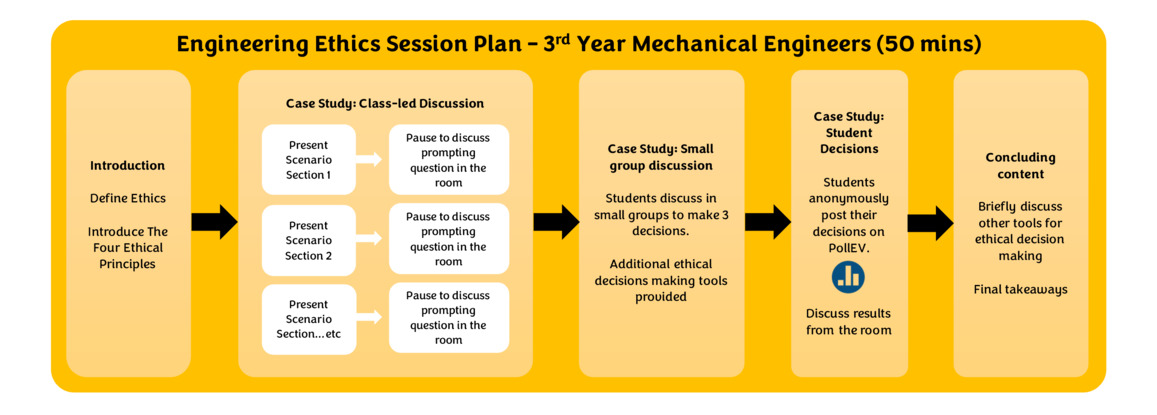
Dr Emma A Taylor, founder of the Engineering Deaf Awareness Project (E-DAP), Royal Academy of Engineering Visiting Professor, Cranfield University, and Professor Sarah Jayne Hitt, PhD SFHEA, NMITE, Edinburgh Napier University, discuss embedding ethics in engineering education through wide use of deaf awareness: a gateway to a more inclusive practice.
“An ethical society is an inclusive society”. This is a statement that most people would find it hard to disagree strongly with. As users of the EPC’s Engineering Ethics Toolkit and readers of this blog we hope our message is being heard loud and clear.
But hearing is a problem:
One in five adults in the UK are deaf, have hearing loss or tinnitus. That is 12 million adults or 20% of the population. In the broader context of‘ ‘communication exclusion’ (practices that exclude or inhibit communication), this population figure may be even larger, when including comprehension issues experienced by non-native speakers and poor communication issues such as people talking over one another in group settings such as during meetings.
This ‘communication exclusion’ gap is also visible in an education context, where many educators have observed group discussion and group project dynamics develop around those who are the most dominant (read: loudest) communicators. This creates an imbalanced learning environment with the increased potential for unequal outcomes. Even though this ‘communication exclusion’ and lack of skills is such a huge problem, you could say it’s hidden in plain sight. Identification of this imbalance is an example of ethics in action in the classroom.
Across all spheres, we suggest that becoming deaf aware is one way to begin to address communication exclusion issues. Simple and practical effective tips are already widely disseminated by expert organisations with deep in the field experience (see list of resources below from RNID). Our collective pandemic experience took us all a great step forward in seeing the benefits of technology, but also in understanding the challenges of communicating through the barriers of technology. As engineering educators we can choose to become more proactive in using tools that are already available, an action that supports a wider range of learners beyond those who choose to disclose hearing or understanding related needs. This approach is inclusive; it is ethical.
And as educators we propose that there is an even greater pressing need to amplify the issue and promote practical techniques towards improving communication. Many surveys and reports from industry have indicated that preparing students for real world work environments needs improving. Although they often become proficient in technical skills, unless they get an internship, students may not develop the business skills needed for the workplace. Communication in all its forms is rightly embedded in professional qualifications for engineers, whether EngTech, IEng, CEng or other from organisations such as the UK’s Engineering Council.
And even when skills are explicitly articulated in the syllabus and the students are assessed, much of what is already being taught is not actually being embedded into transferable skills that are effectively deployed in the workplace. As education is a training ground for professional skills, a patchy implementation of effective and active practice of communication skills in the education arena leads to variable skill levels professionally.
As engineers we are problem solvers, so we seek clarification of issues and derivation of potential solutions through identification and optimisation of requirements. The problem-solving lens we apply to technology can also be applied to finding ways to educate better communicators. The “what” is spoken about in generic terms but the “how”, how to fix and examine root causes, is less often articulated.
So what can be done? What is the practical framework that can be applied by both academics and students and embedded in daily life? And how can deaf awareness help get us there?
Our proposal is to work to embed and deploy deaf awareness in all aspects of engineering education. Not only because it is just and ethical to do so, but because it can help us see (and resolve) other issues. But this won’t, and can’t, be done in one step. Our experience in the field shows that even the simplest measures aren’t broadly used despite their clear potential for benefit. This is one reason why blogs and toolkits like this one exist: to help educators embed resources and processes into their teaching practice.
It’s important to note that this proposal goes beyond deaf awareness and is really about reducing or removing invisible barriers that exist in communication and education, and addressing the communication problem through an engineering lens. Only when one takes a step back with a deaf awareness filter and gets the relevant training, do your eyes (and ears) open and see how it helps others. It is about improving the effectiveness of teaching and communication.
This approach goes beyond EDI principles and is about breaking barriers and being part of a broader student development approach, such as intellectual, emotional, social, and personal growth. The aim is to get students present and to be in the room with you, during the process of knowledge transfer.
As we work on making our engineering classrooms better for everyone, we are focusing on understanding and supporting students with hearing impairments. We are taking a step back and getting re-trained to have a fresh perspective. This helps us see things we might have missed before. The goal is not just to be aware but to actually improve how we teach and communicate.
We want our classrooms to be inclusive, where everyone’s needs are considered and met. It is about creating an environment where all our students, including those with hearing impairments, feel supported and included in the learning process. And stepping back and taking a whole human (“humanist”) view, we can define education as an endeavour that develops human potential—not just an activity that produces nameless faceless quantifiable outcomes or products. As such, initiatives such as bringing forward deaf awareness to benefit broader communication and engagement provide a measurable step forward into bringing a more humanistic approach to Engineering Education.
So what can you do?
- The first step is always awareness. Inform yourself, raise awareness amongst yourself and your colleagues, and make improvements where you can in your daily education practice
- Consider how you might incorporate deaf awareness in your teaching case studies, and consider how deaf awareness can improve the quality of your group work discussions
Through the EPC’s growing efforts on EDI, we welcome suggestions for case studies and other teaching materials and guidance that bring together ethics, sustainability and deaf awareness (or other issues of inclusivity).
We’re pleased to report that we are aiming to launch an EDI Toolkit project soon, building on the work that we’ve begun on neurodiversity. Soon we’ll be seeking people to get involved and contribute resources, so stay tuned! (i.e. “If you have a process or resource that helped your teaching become more inclusive, please share it with us!”).
RNID resources list
- Talking about hearing loss at work – RNID
- How to make your workplace inclusive for deaf staff and staff with hearing loss and tinnitus – RNID
- Make your meetings deaf aware – RNID
- How to communicate with someone who is deaf or has hearing loss – RNID
- Communication support – RNID – includes information on how to book communication support
- Health and safety for deaf staff and staff with hearing loss – RNID
- Technology and assistive devices – RNID – this has links on how to use accessibility features on video conferencing apps as well as how to use video captions on social media
- Prevalence of deafness and hearing loss
- Information and support
Other resources
- Engineering Deaf Awareness Project (E-DAP) Toolkit
- What does deaf awareness have to do with educating engineers more effectively?
- Educating risk, enabling deaf awareness
- Engineering skills needs – now and into the future
- Engineers 2030: redefining the engineer of the 21st century / Future skills needs– a review of the literature
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.
This article is also available here.