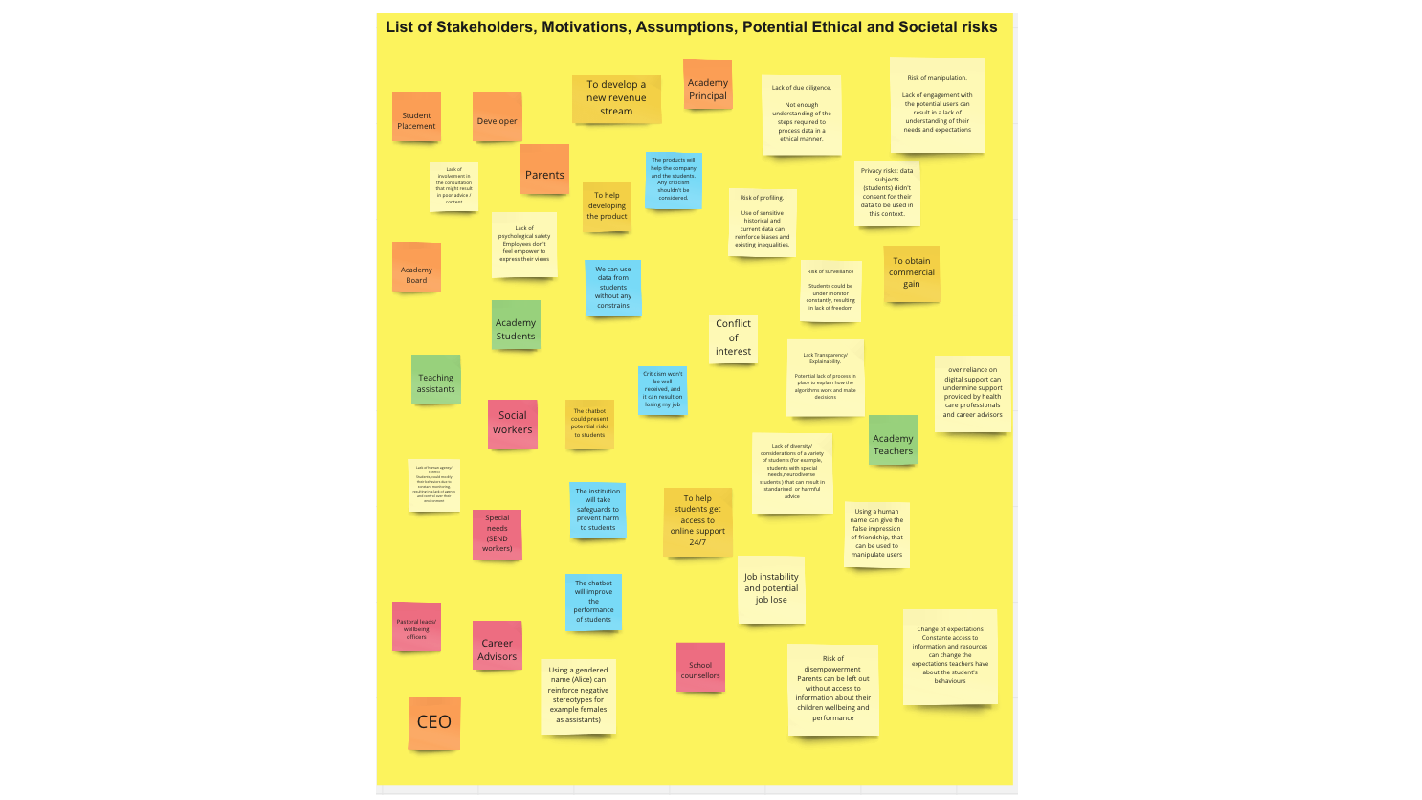
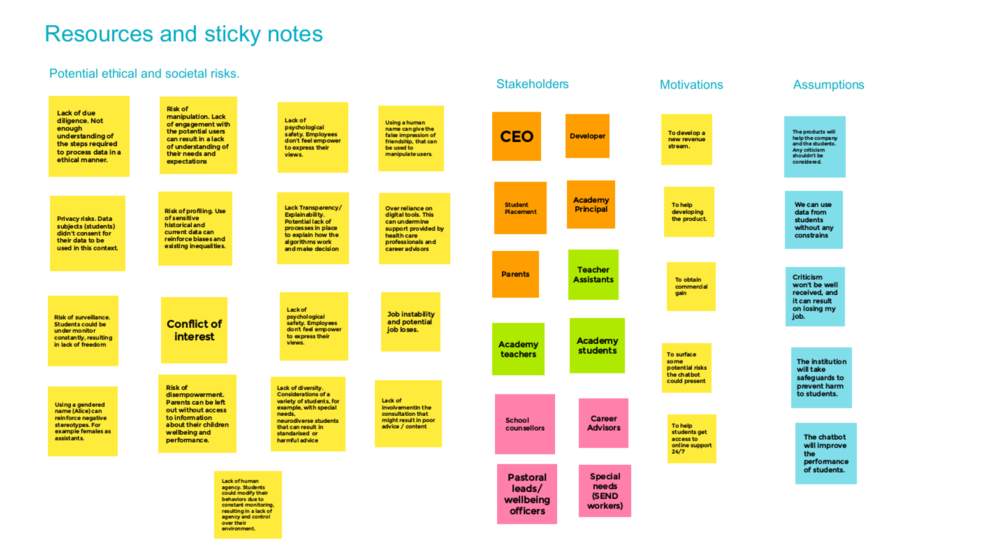
Case enhancement: Facial recognition for access and monitoring
Case enhancement: Facial recognition for access and monitoring
Activity: Prompts to facilitate discussion activities.
Author: Sarah Jayne Hitt, Ph.D. SFHEA (NMITE, Edinburgh Napier University).
Overview:
There are several points in this case during which an educator can facilitate a class discussion about relevant issues. Below are prompts for discussion questions and activities that can be used. These correspond with the stopping points outlined in the case. Each prompt could take up as little or as much time as the educator wishes, depending on where they want the focus of the discussion to be. The discussion prompts for Dilemma Part three are already well developed in the case study, so this enhancement focuses on expanding the prompts in Parts one and two.
Dilemma Part one – Discussion prompts:
1. Legal Issues. Give students ten minutes to individually or in groups do some online research on GDPR and the Data Protection Act (2018). In either small groups or as a large class, discuss the following prompts. You can explain that even if a person is not an expert in the law, it is important to try to understand the legal context. Indeed, an engineer is likely to have to interpret law and policy in their work. These questions invite critical thinking and informed consideration, but they do not necessarily have “right” answers and are suggestions that can help get a conversation started.
a. Are legal policies clear about how images of living persons should be managed when they are collected by technology of this kind?
b. What aspects of these laws might an engineer designing or deploying this system need to be aware of?
c. Do you think these laws are relevant when almost everyone walking around has a digital camera connected to the internet?
d. How could engineers help address legal or policy gaps through design choices?
2. Sharing Data. Before entering into a verbal discussion, either pass out the suggested questions listed in the case study on a worksheet or project on a screen. Have students spend five or ten minutes jotting down their personal responses. To understand the complexity of the issue, students could even create a quick mind map to show how different entities (police, security company, university, research group, etc.) interact on this issue. After the students spend some time in this personal reflection, educators could ask them to pair/share—turn to the person next to them and share what they wrote down. After about five minutes of this, each pair could amalgamate with another pair, with the educator giving them the prompt to report back to the full class on where they agree or disagree about the issues and why.
3. GDPR Consent. Before discussing this case particularly, ask students to describe a situation in which they had to give GDPR consent. Did they understand what they were doing, what the implications of consent are, and why? How did they feel about the process? Do they think it’s an appropriate system? This could be done as a large group, small group, or through individual reflection. Then turn the attention to this case and describe the change of perspective required here. Now instead of being the person who is asked for consent, you are the person requiring consent. Engineers are not lawyers, but engineers often are responsible for delivering legally compliant systems. If you were the engineer in charge in this case, what steps might you take to ensure consent is handled appropriately? This question could be answered in small groups, and then each group could report back to the larger class and a discussion could follow the report-backs.
4. Institutional Complexity. The questions listed in the case study relate to the fact that the building in which the facial recognition system will be used accommodates many different stakeholders. To help students with these questions, educators could divide the class into small groups, with each group representing one of the institutions or stakeholder groups (college, hospital, MTU, students, patients, public, etc.). Have each group investigate whether regulations related to captured images are different for their stakeholders, and debate if they should be different. What considerations will the engineer in the case have to account for related to that group? The findings can then be discussed as a large class.
Dilemma Part two – Discussion prompts:
The following questions relate to macroethical concerns, which means that the focus is on wider ethical contexts such as fairness, equality, responsibility, and implications.
1. Benefits and Burdens. To prepare to discuss the questions listed in the case study, students could make a chart of potential harms and potential benefits of the facial recognition system. They could do this individually, in pairs or small groups, or as a large class. Educators should encourage them to think deeply and broadly on this topic, and not just focus on the immediate, short-term implications. Once this chart is made, the questions listed in the case study could be discussed as a group, and students asked to weigh up these burdens and benefits. How did they make the choices as to when a burden should outweigh a benefit or vice versa?
2. Equality and Utility. To address the questions listed in the case study, students could do some preliminary individual or small group research on the accuracy of facial recognition systems for various population groups. The questions could then be discussed in pairs, small groups, or as a large class.
3. Engineer Responsibility. Engineers are experts that have much more specific technical knowledge and understanding than the general public. Indeed, the vast majority of people have no idea how a facial recognition system works and what the legal requirements are related to it, even if they are asked to give their consent. Does an engineer therefore have more of a responsibility to make people aware and reassure them? Or is an engineer just fulfilling their duty by doing what their boss says and making the system work? What could be problematic about taking either of those approaches?
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.