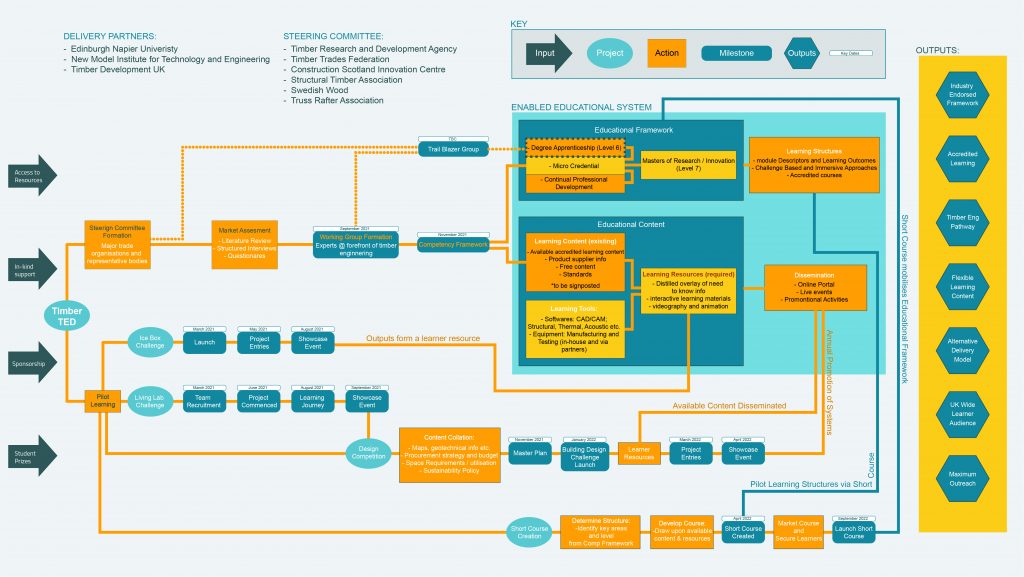
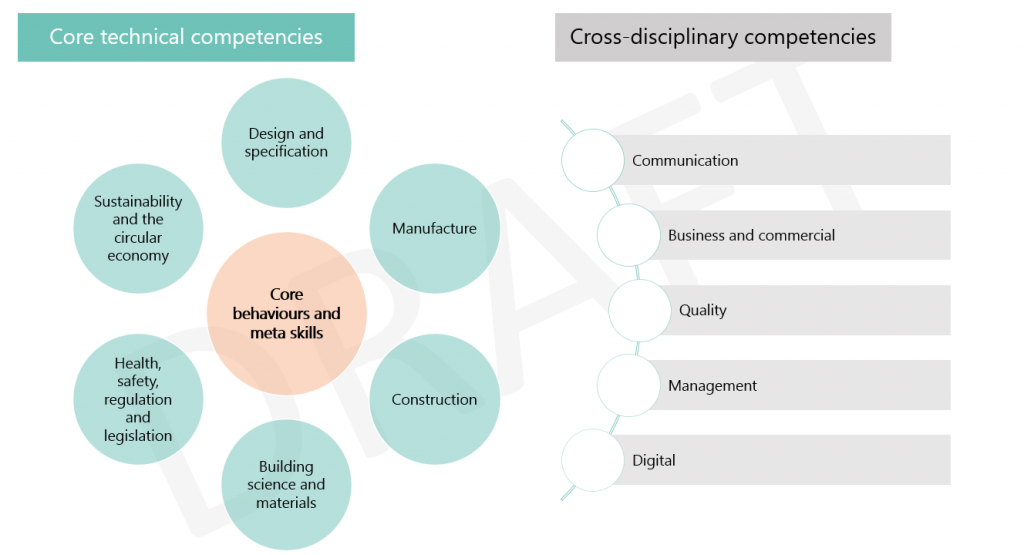
Theme: Universities’ and business’ shared role in regional development; Knowledge exchange.
Theme: Universities’ and business’ shared role in regional development; Knowledge exchange.
Authors: Prof Tony Dodd (Staffordshire University); Marek Hornak (Staffordshire University) and Rachel Wood (Staffordshire University).
Keywords: Regional Development Funding, Innovation Enterprise Zone
Abstract: The Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire region registers low in measures of economic prosperity, research and development expenditure, productivity, and higher skills. Staffordshire University has received funding to support regional growth in materials, manufacturing, digital and intelligent mobility and to develop higher skills. Packaged together into the Innovation Enterprise Zone these projects have made positive impacts in the region. This presentation will provide an overview of our approach to regional support and highlight impact and lessons learnt for companies, academics, and students.
Background
The Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire economy underperforms compared to the wider West Midlands and England [1].
- Below average productivity – £19,114 produced per person (£27,660 in England) (2017)
- Below average higher skills – Level 4+ is 33.4% (39.2% for the UK)
- Below average R&D expenditure ranking 29th out of 38 in LEPs for overall R&D expenditure and 23rd out of 38 for R&D expenditure per full-time employee (2013)
- 38 new business start-ups per 10,000 people which is below regional and national averages
- Business density of 410 business per 10,000 population – lower than regional and national averages
Industry is dominated by SMEs with strengths in manufacturing, advanced materials, automotive, logistics and warehousing, agriculture, and digital industries [1].
Aims and Objectives
The aim was to develop an ecosystem for driving innovation, economic growth, job creation and higher skills in Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire.
The objectives were to:
- Support regional SMEs to improve innovation through knowledge transfer.
- Increase employment and productivity.
- Increase the number of products/services to the companies and market.
- Enhance student experience and employability through placement opportunities
- Enhance higher skills to support long term innovation in the region.
Enterprise Zone and Projects
Funding was successfully awarded from ERDF, Research England, and Staffordshire County Council. The themes of the projects were developed in collaboration with regional partners to identify key strengths and potential for growth. Each of the projects is match funded by Staffordshire University including through academic time.
Innovation
- Staffordshire Advanced Manufacturing, Prototyping, and Innovation Demonstrator (ERDF) to support innovation in manufacturing and product development. (Note: this project has now ended.)
- Staffordshire Connected & Intelligent Mobility Innovation Accelerator (ERDF) to deliver innovation in connected and intelligent mobility.
- Staffordshire Digital Innovation Partnerships (ERDF, Staffordshire County Council) to support digital transformation and address social challenges through digital solutions.
- Innovation and Productivity Pathfinder (UK Government Community Renewal Fund) to review innovation challenges and develop bespoke innovation plans.
Skills development through the Enterprise Academy
- Staffordshire Higher Skills and Engagement Pathways (ESF) providing fully funded continuing professional development.
- Staffordshire E-Skills and Entrepreneurship Gateway (ESF) to develop digital skills and entrepreneurship in SMEs, students and graduates.
The projects are part of the wider Staffordshire University Innovation Enterprise Zone (launched November 2020, Research England) to support research collaboration, knowledge exchange, innovation, and skills development. This includes space for business incubation and low-cost shared office space in The Hatchery for new start-ups. We also provide a Creative Lab (funded by Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire LEP) for hosting business-academic meetings and access to the SmartZone equipment for rapid prototyping.
Spotlight on Innovation Projects
To highlight the differences between approaches we highlight two innovation projects.
| Staffordshire Advanced Manufacturing, Prototyping, and Innovation Demonstrator (SAMPID) | Staffordshire Connected & Intelligent Mobility Innovation Accelerator (SCIMIA) |
|---|---|
| Advanced manufacturing and product development | Connected and intelligent mobility |
| ERDF funded | ERDF funded |
| SMEs in Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire | SMEs in Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire |
| 12-weeks of funded support | Up to 12-months of support |
| Innovation consultants (students/graduates) | Innovation consultants (students/graduates) |
| Academic supervision, knowledge exchange and business support | Academic supervision, knowledge exchange and business support |
| Dedicated technician support (0.5FTE) | Dedicated technician support (0.5FTE) |
| 3x funded PhD students to support projects and develop advanced innovation | 2x Innovation and Enterprise Fellows to support technical business engagement |
| Funded advanced manufacturing equipment (including 3D metal printing, robot arms) and access to equipment in SmartZone | Access to equipment in SmartZone |
- Business engagement is initiated through business development managers.
- Academics are involved in early discussions to ensure expertise is available.
- Students are interviewed by the company, academic and programme manager.
Case study videos:
Lessons Learnt
Business engagement
- Businesses are often engaging with a university for the first time.
- Equipment purchased (SAMPID) has attracted companies to engage and supported innovation. The equipment would not normally be available to SMEs and enhanced the ability for rapid prototyping.
- It is important to manage company expectations from the outset in terms of what is achievable in the timescales using undergraduate students.
- Engagement with academics during project development is important to understand what is technically achievable.
- Projects work best where there is active engagement from the business who have experts to support the student and challenge the direction of the project.
Project length
- Recruiting students for the longer 6/12-month SCIMIA projects has proven more difficult due to the commitment and difficulty of fitting projects around studies.
- Shorter 12-week, 15 hours per week, SAMPID projects fit more naturally around undergraduate studies so are easier to recruit to.
- 12-week projects have exceeded expectations with complex prototypes developed.
Student roles and recruitment
- Students have exceeded expectations, and several have their work extended beyond the project.
- Direct marketing to students on the opportunities available is important to raising awareness.
- Unsuccessful students are targeted for future projects based on their skill set.
- Unitemps minimise the burden of recruiting students.
Supporting roles
- The innovation and enterprise fellows’ positions (SCIMIA) require technical and business experience. They have proven invaluable in engaging with companies alongside business development managers to better understand the technical requirements and to help companies think about what innovations are most valuable.
- Technician recruitment has proven difficult for all projects due to the posts being 0.5FTE and fixed term.
- It is important for business development managers and programme managers to ensure a smooth transition of the company relationship.
- PhD students (SAMPID) have allowed more advanced innovations to be explored in areas of manufacturing and product development that have fed into projects.
Academic involvement
- Pioneer academics who could demonstrate the positive impacts to their research and students and the programme manager developing a close relationship with a pool of academics has been key to ensuring academic engagement.
- Some projects have led to academic research and publications which we will explore further.
Possible future developments
- Peer mentoring to support students new to the innovation projects.
- Formal training for student innovators in design thinking and systems/requirement engineering.
- Developing successful relationships into Knowledge Transfer Partnerships, InnovateUK funding and support for EPSRC projects.
References
[1] Stoke-on-Trent and Staffordshire Local Enterprise Partnership (2019). Local Industrial Strategy – Evidence Base September 2019. Available from Development of a Stoke-on-Trent & Staffordshire Industrial Strategy (SSIS) (stokestaffslep.org.uk)
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.