Author: Jing Zhao (University of West of England).
Topic: Investigating the decarbonisation transition.
Type: Teaching.
Relevant disciplines: Civil; Structural; Chemical; Mechanical; Electrical; Computing.
Keywords: Decarbonisation, Housing, Built environment; Net zero, Carbon emissions; Energy efficiency; Sustainable energy; Local community; Curriculum; Higher education; Sustainability; Assessment.
AHEP mapping: This resource addresses two of the themes from the UK’s Accreditation of Higher Education Programmes fourth edition (AHEP4): The Engineer and Society (acknowledging that engineering activity can have a significant societal impact) and Engineering Practice (the practical application of engineering concepts, tools and professional skills). To map this resource to AHEP outcomes specific to a programme under these themes, access AHEP 4 here and navigate to pages 30-31 and 35-37.
Related SDGs: SDG 4 (Quality education); SDG 7 (Affordable and clean energy); SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure); SDG 11 (Sustainable cities and communities).
Educational level: Beginner.
Learning and teaching notes:
The purpose of this exercise is to encourage students to think in a socio-technical perspective of delivering extreme low carbon housing (e.g. Passivhaus), in order to support the occupants in adapting to new technologies and low-carbon lifestyle, shifting the paradigm from building isolated energy efficient homes to forming low-carbon communities.
Learners have the opportunity to:
- Practice stakeholder engagement;
- Consider physiological and ecological effects of engineering design and technology;
- Practice communication in multiple modes;
Teachers have the opportunity to:
- Integrate technical learning on energy-efficient buildings such as emerging technologies and sustainability analysis;
- Highlight the effects that engineering design and technology has on human behaviour;
- Informally evaluate collaboration, critical thinking, and communication.
Supporting resources:
- Humphreys, M.A., Fergus Nicol, J. (2018). Principles of Adaptive Thermal Comfort. In: Kubota, T., Rijal, H., Takaguchi, H. (eds) Sustainable Houses and Living in the Hot-Humid Climates of Asia. Springer, Singapore 103–113.
Terminology:
Before beginning the activity, teachers and learners will want to become familiar with the following concepts.
- Performance gap: A performance gap is a disparity that is found between the energy use predicted and carbon emissions in the design stage of buildings and the energy use of those buildings in operation.
- Rebound effect: The rebound effect deals with the fact that improvements in efficiency often lead to cost reductions that provide the possibility to buy more of the improved product or other products or services (Thiesen et al., 2008).
- Adaptive comfort: The adaptive approach to thermal comfort recognises that people are not passive with regard to their thermal environment, but actively control it to secure comfort. Thermal comfort can thus be seen as a self-regulating system, incorporating not only the heat exchange between the person and the environment but also the physiological, behavioural and psychological responses of the person and the control opportunities afforded by the design and construction of the building (Humphreys & Nicol, 2018).
- Energy behaviour: Energy behaviour denotes behaviour or behavioural patterns related to energy use. Research has stressed the important role occupants play in determining the energy use of buildings (Janda, 2011).
- Usability and control: This presents how accessible and user-friendly the control systems are in a building. For instance, where the control panels are located, how easy it is to open a window, or to understand the control panel. (Stevenson et al., 2013).
- Resident engagement plan: A resident engagement plan or strategy maps out a path to communicate and support residents for general or specific tasks. Examples can be found here (Home Upgrade Hub, 2022 p20 and p30; Social Housing Retrofit Accelerator, n.d.)
Activity overview:
Students will role-play the post occupancy stage of inhabiting a Passivhaus home by playing different characters with different priorities (and personalities). Students will need to learn what new technologies and features are included in Passivhaus and what difficulties/problems the residents might encounter, and at the same time familiarise themselves with contemporary research on energy behaviour, performance gap, rebound effect, as well as broader issues in decarbonisation transition such as social justice and low carbon community building. Through two community meetings, the community manager needs to resolve the residents’ issues, support the residents in learning and adapting their behaviours, and devising an engagement plan to allow the residents to form a self-governed low-carbon community.
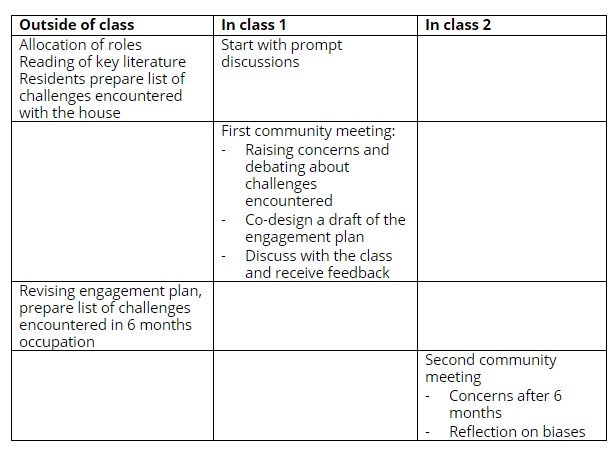
Step one: Preparation prior to class:
Provide a list of reading materials on ‘performance gap’, ‘rebound effect’, ‘adaptive comfort’, energy behaviour, usability and control literature, as well as on Passivhaus and examples of low-carbon features and technologies involved to get a sense of what difficulties residents might encounter.
To prepare for the role-play activity, assign students in advance to take on different roles (randomly or purposefully), or let them self-assign based on their interests. They should try to get a sense of their character’s values, lifestyle, priorities, abilities. Where no information is available, students can imagine the experiences and perspectives of the residents. Students assigned to be community managers or building associations will prepare for the role-play by learning about the Passivhaus system and prepare ways to support occupants’ learning and behaviour adaptation. The goal is to come up with an engagement plan, facilitate the residents to form their own community knowledge base and peer support. (Considering 1. Who are you engaging (types of residents and their characteristics); 2. How are you engaging (level of engagement, types of communication; 3. When are you engaging (frequency of engagement)
Step two: In class, starting by giving prompts for discussions:
Below are several prompts for discussion questions and activities that can be used. Each prompt could take up as little or as much time as the educator wishes, depending on where they want the focus of the discussion to be.
- Discuss what support the residents might need in post occupancy stage? Who should provide (/pay for) the support? For how long? Any examples or best practice that they might know? Does support needs to be tailored to specific groups of people? (see extra prompts at the end for potential difficulties)
- Discuss what the risks are involved in residents not being sufficiently supported to adapt their behaviour when living in a low-carbon house or Passivhaus? (reflect on literature)
- Discuss what are the barriers to domestic behaviour change? What are the barriers to support the residents in changing behaviour and to build low-carbon community?
Step three: Class 1 Role Play
Prior to the Role Play, consider the following prompts:
Consider the variety of residents and scenarios:
Their varying demographics, physical and mental abilities, lifestyle and priorities. The following characters are examples. Students can make up their own characters. Students can choose scenarios of
1) social housing or;
2) private owner-occupier
Social housing tenants will likely have a more stretched budget, higher unemployment rate and a bigger proportion of disabled or inactive population. They will have different priorities, knowledge and occupancy patterns than private owner-occupier, and will be further disadvantaged during decarbonisation transition (Zhao, 2023). They will need different strategies and motivations to be engaged. The characters of residents could be chosen from a variety of sources (e.g. RIBA Brief generator), or based on students’ own experiences. Each character needs to introduce themselves in a succinct manner.
Other stakeholders involved include:
- Developer/ housing association/ council
- Passivhaus designer/architect
- Engineer
- Community/property manager
They are role-specific characters that don’t necessarily need a backstory. They are there to listen, take notes, give advice and come up with an engagement plan.
Consider the post occupancy in different stages:
- Prior to move-in
- Move-in day
- The initial month
- Change of season
- Quarterly energy audit meeting
Consider the difficulties the residents might encounter:
- Where is the thermostat?
- Where is the radiator?
- How do I increase the temperature in the room?
- It’s very stuffy and hot in the south-facing bedroom
- What does the MVHR do?
- Why is the MVHR so noisy?
- Does PV panel supply electricity to my washing machine? When should I put my washing on?
- Do I get paid from the electricity generated from the PV panel?
- Why is my energy bill higher than expected?
Consider the different engagement levels of the residents:
- 20-60-20: 20% very engaged, 60% follows, 20% not engaged
- How do you ensure the maximum level of satisfaction from all residents, including the ones not so engaged?
- How to encourage the residents to take ownership and responsibility?
The role-play consists of two community meetings over two classes. The first meeting is held at two weeks after move-in date. The second meeting at 6 months of occupancy. The meeting should include a variety of residents on one side, and the ‘chair’ of the meeting on the other. (Consider the accessibility and inclusivity of the meetings as when and where those will be held). In the first meeting, residents will get to know each other, ask questions about house-related problems occurred in the first two weeks, voice concerns. Community managers/council members will chair the meeting, take notes and make plans for support. The teacher should act as a moderator to guide students through the session. First the teacher will briefly highlight the issue up for discussion, then pass it to the ‘chair’ of the meeting. The ‘chair’ of the meeting will open the meeting with the purpose of the meeting – to support the residents and facilitate a self-governed low carbon community. They then ask the residents to feedback on their experience and difficulties. At the end of the first meeting, the group of students will need to co-design an engagement plan, including setting agendas for the second meeting in a 6-month interval (but in reality will happen in the second class) and share the plan with the residents and the class. The teacher and class will comment on the plan. The group will revise the plan after class so it’s ready for the second meeting.
Step four: Homework tasks: Revising the plan
The students will use the time before the second class to revise the plan and prepare for challenges, problems occurred over the 6-months period.
Optional wild cards could be used as unpredictable events occur between the first and second meeting. Such events include:
- Energy price dramatically increase (or decrease)
- Heat wave
- Heavy rain for three months (no solar gain)
- Whole grid decarbonisation (might affect occupants with gas central heating)
Step five: Class 2 Role play
The second meeting in the second class will either be chaired by community managers/council members, or be chaired by a few residents, monitored by community managers/council members. The second meeting begins the same way. The students playing residents should research/imagine problems occurred during the 6 months period (refer to literature), and what elements of the engagement plan devised at the end of the first meeting worked and what hasn’t worked. The ‘chair’ of the meeting will take notes, ask questions or try to steer the conversations. At the end of the second meeting, the ‘chair’ of the meeting will reflect on the support and engagement plan, revise it and make a longer-term plan for the community to self-govern and grow. At the end of this class, the whole class could then engage in a discussion about the outcome of the meetings. Teachers could focus on an analysis of how the process went, a discussion about broader themes of social justice, community building, comfort, lifestyle and value system. Challenge students to consider their personal biases and position at the outset and reflect on those positions and biases at the end of the meeting.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.
To view a plain text version of this resource, click here to download the PDF.