Case enhancement: Power-to-food technologies
Case enhancement: Power-to-food technologies
Activity: An ethical evaluation of the technology and its impacts.
Author: Dr Fiona Truscott (UCL).
Overview:
This enhancement is for an activity found in the Dilemma Part one, Point 1 section of the case: “Identify different aspects of the production process where ethical concerns may arise, from production to delivery to consumption.” Below are prompts for discussion questions and activities that can be used. Each prompt could take up as little or as much time as the educator wishes, depending on where they want the focus of the discussion to be.
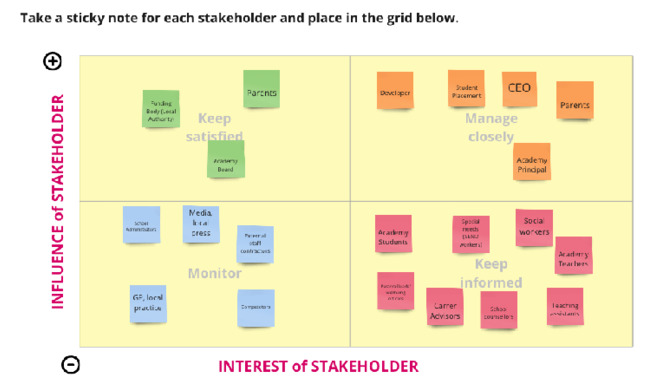
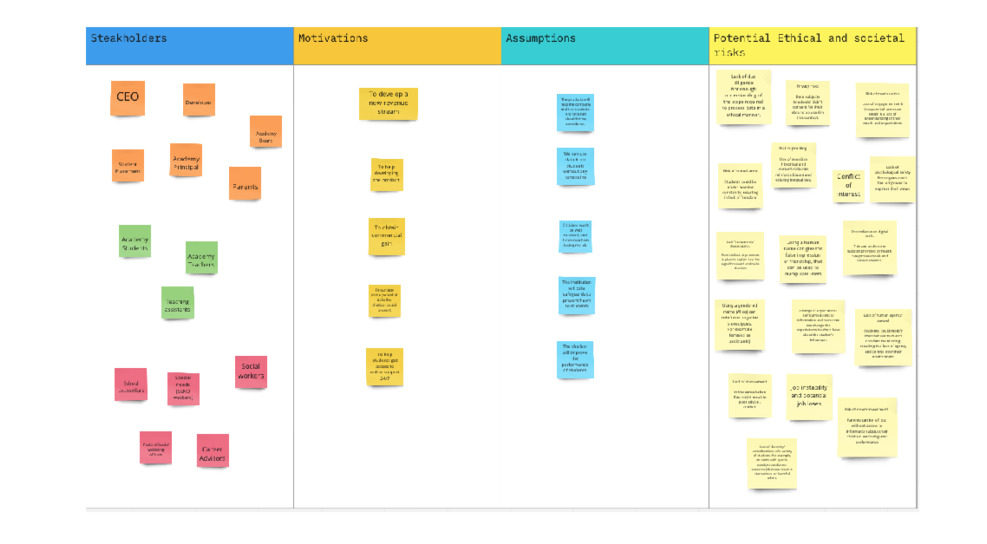
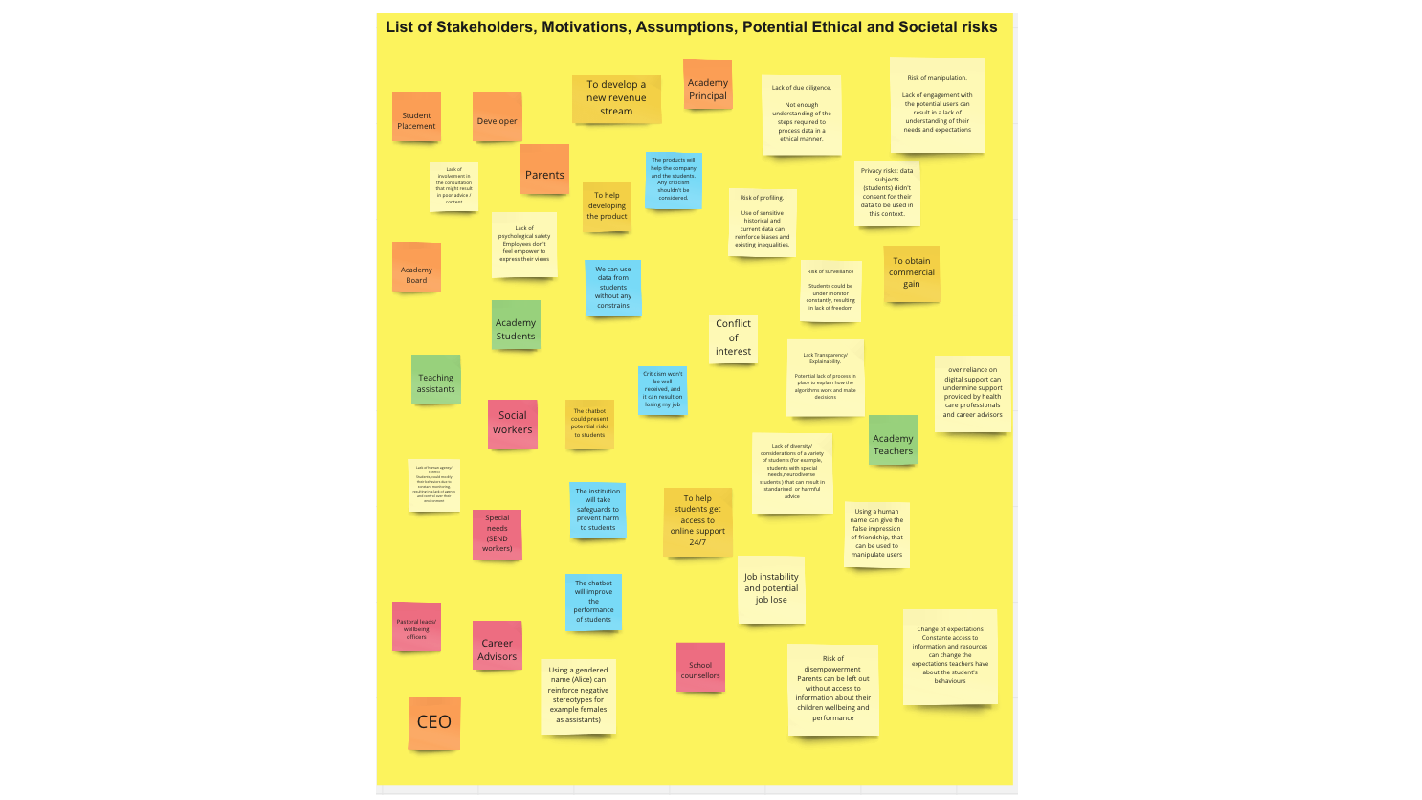
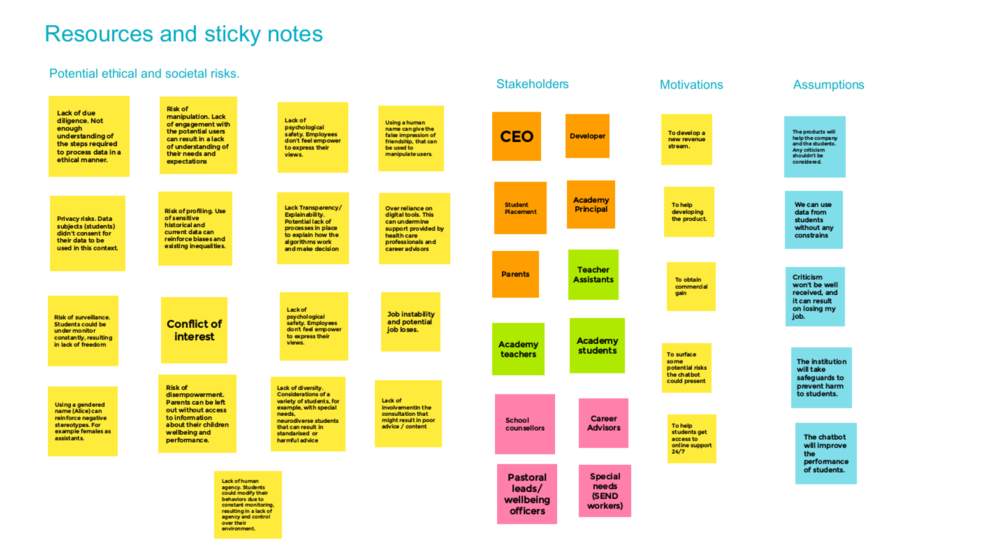
In this group activity, students will act as consultants brought in by the Power to Food team to create an ethical evaluation of the technology and any impacts it may have throughout its lifetime. The aim here is for students to work together to discuss the potential ethical issues at each stage of the production process as well as thinking about how they might be addressed. Groups will need to do research, either in class or at home. Depending on the timeframe you may want to give them a starting point and some basic information found in the case study’s learning and teaching resources.
Suggested timeline:
- Introduce students to the Power to Food case study (this could be pre-reading) and what they will be doing in their teams.
- Some facilitated workshop time/space for Q&As; this may be more or less open-ended depending on where your students are in their programme. Depending on time, you may want to centre workshops around harms or values or a particular stage of the production process. You can use the questions below to structure a discussion session or get teams to look at alternative viewpoints.
- Teams present/submit their work.
Team briefing:
You are a team of consultants brought in by the company who has developed Power to Food technology. Before they go to market they want to understand the ethical issues that may arise from the technology and address them if possible. They want you to look at the process as a whole and identify any ethical issues that might come up. They also want to know how easy these issues might be to address and want you to suggest potential ways to address them. You will need to provide the company with a briefing on your findings.
Tools:
It’s useful to give teams some frameworks through which they can do an analysis of the production process. One of those is to discuss who is harmed by the process at each stage. This is harm in the widest possible sense: physical, environment, political, reputational etc. What or who could be impacted and how? Another framework is the values of the people or entities involved in the process: what are they trying to achieve or what do they want and are any of these in conflict? Topics such as sustainability and accessibility also have an ethical dimension, and using these as a lens can help students to look at the problem from a different viewpoint.
Prompts for questions:
These are questions that you can get students to answer in class or suggest that they cover in an assessment. This could also be information you give the team so that they can use it as a foundation.
- Identify the different stages of the Power to Food production process and the contexts that they happen in.
- What harms might happen in each stage? Who or what might be harmed, how likely is it and what impact would it have?
- What values might each person or entity that is involved with each have? What would they want and what are their responsibilities? Is there conflict between these?
- Is there anything outside of harms and values that might cause an ethical issue?
- What happens if you use a sustainability lens? Or a risk lens? What about accessibility?
- Think about how you might address these ethical issues. Sort your identified ethical issues out into those that might be easy to address and those that aren’t.
- Why are some easier than others to address?
Assessment:
This group activity lends itself to a few different assessment formats, depending on what fits with your programme and timeframe. The two key things to assess are whether students can understand and identify ethical issues across the whole Power to Food production process and whether they can discuss ways to address these issues and the complexities that can be involved in addressing these issues. These two things can be assessed separately; for example through a written report where teams discuss the potential issues and a presentation where they talk about how they might address these issues. Or one assessment can cover both topics. This can be a written report, a live or recorded presentation, a video, podcast or a poster. Teams being able to see other teams’ contributions is both a good way of getting them to discuss different viewpoints and makes for a fun session. You can get teams to present their final work or a draft to each other.
Depending on the timeframe, you may also want to build in some skills assessment too. The AAC&U’s VALUE rubrics are a great starting point for assessing skills and IPAC is a good tool for assessing teamwork via peer assessment.
Marking Criteria:
| Good | Average | Poor | |
| Understanding and identification of ethics issues across the whole Power to Food production process | Has identified and understood context specific ethical issues across the production process. May have shown some understanding of how issues may impact on each other. | Has identified and understood broad/general ethical issues around production processes but hasn’t linked much to the specific context of the case study. Some stages may be more detailed than others. | Has not identified many or any ethical issues and seems to have not understood what we’re looking for. |
| Discussing ways to address these issues and the complexities that can be involved | Has identified context specific ways to address the ethical issues raised and has understood the potential complexities of addressing those ethical issues. | Has identified broad/general ways to address the ethical issues raised and made some reference to differing levels of complexity in addressing ethical issues. | Has not identified many or any ways to address the ethical issues raised and seems to have not understood what we’re looking for. |
| Communication | Very clear, engaging and easy to understand communication of the ethical issues involved and ways to address them. Right language level for the audience. | Generally understandable but not clear in places or uses the wrong level of language for the audience (assumes too much or not enough prior knowledge). | Difficult to understand the point being made either due to language used or disconnection to the point of the assessment or topic. |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Any views, thoughts, and opinions expressed herein are solely that of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, policies, or position of the Engineering Professors’ Council or the Toolkit sponsors and supporters.